
Table of Contents
Introduction:

Water bills climbing higher every month? Watching precious rainfall disappear down storm drains while your garden thirsts for moisture? Rainwater harvesting offers an elegant solution that transforms wasted precipitation into a valuable resource right on your property. This ancient practice has evolved into modern water conservation systems that can slash utility costs while boosting your home’s sustainability, which is why The Ultimate Rainwater Harvesting Guide 2025 has become essential reading for eco-conscious homeowners.
Whether you’re motivated by environmental concerns, rising water costs, or simply want backup water security, understanding rainwater collection basics opens doors to significant household improvements. The Ultimate Rainwater Harvesting Guide 2025 reveals that modern systems range from simple $50 rain barrels to sophisticated whole-house installations, making this technology accessible to virtually every homeowner regardless of budget or technical expertise.
As outlined in The Ultimate Rainwater Harvesting Guide 2025, these innovative systems not only reduce dependency on municipal water supplies but also provide sustainable solutions for irrigation, emergency water storage, and long-term cost savings. Following the comprehensive strategies detailed in The Ultimate Rainwater Harvesting Guide 2025, homeowners can implement effective water conservation measures that deliver both immediate and long-term benefits for their properties and the environment.
What is Rainwater Harvesting? Understanding the Fundamentals

Rainwater harvesting definition encompasses any systematic approach to collecting, filtering, and storing precipitation for later use. The practice captures water that would otherwise become stormwater runoff, treating it appropriately for intended applications ranging from garden irrigation to household water supply.
The water collection basics revolve around four essential elements working in harmony. Catchment surfaces, typically rooftops, gather precipitation and channel it toward collection points. Conveyance systems including gutters and downspouts transport water from collection areas to storage locations. Treatment components filter and purify collected water to appropriate quality standards. Storage vessels hold treated water until needed for various household applications.
Historical context reveals that civilizations have practiced rainwater collection for over 4,000 years. Ancient Romans built massive underground cisterns that supplied entire cities. Desert communities in the Middle East perfected collection techniques that sustained populations in arid climates. Mediterranean cultures integrated water storage solutions into architectural designs that remain functional today.
Modern applications have transformed these ancient concepts using contemporary materials and automation technology. Today’s systems incorporate smart sensors, automated filtration, and seamless integration with existing plumbing infrastructure. Sustainable water practices now combine traditional wisdom with cutting-edge technology to create highly efficient collection networks.
Basic components overview includes catchment areas where rain falls and collects, usually rooftops but also driveways and specially designed surfaces. Gutters and downspouts form the conveyance network that channels water toward storage areas. Filtration systems remove debris and contaminants while storage tanks hold treated water for distribution. Simple gravity-fed systems work for basic applications, while pump systems provide pressurized delivery throughout properties.
The beauty of modern rainwater harvesting systems lies in their scalability and adaptability. Homeowners can start with basic rain barrel setups costing under $100, then gradually expand into comprehensive systems providing substantial household water independence. Each component serves specific functions while contributing to overall system efficiency and reliability.
Why Rainwater Harvesting Matters: Compelling Environmental and Economic Benefits

Rainwater harvesting benefits extend far beyond simple water collection, creating positive impacts that ripple through households, communities, and entire watersheds. Understanding these advantages helps homeowners make informed decisions about implementing water conservation systems that deliver both immediate and long-term value.
Water conservation advantages become immediately apparent in monthly utility bills. Typical residential systems reduce municipal water consumption by 30-50%, translating to substantial annual savings. A standard home can collect over 40,000 gallons yearly from a 2,000 square foot roof in areas receiving moderate rainfall. This collected volume represents hundreds of dollars in avoided water costs annually.
Environmental impact reduction occurs through multiple interconnected pathways. Stormwater management improves significantly when rainfall gets captured rather than contributing to overwhelming municipal drainage systems. Urban flooding decreases as more properties implement collection systems that slow peak runoff rates. Water cycle restoration benefits entire watersheds as reduced runoff allows more natural groundwater recharge.
Sustainable living advantages include increased resilience during drought periods and reduced dependence on stressed municipal water supplies. Many regions face growing water scarcity as populations expand while water sources remain static. Rainwater collection provides local water security that doesn’t strain regional resources or require energy-intensive long-distance transportation.
Emergency water supply benefits become crucial during natural disasters or infrastructure failures. Power outages that disable municipal pumping stations don’t affect gravity-fed rainwater systems. Contamination events that compromise public water supplies leave rainwater users with continued access to safe water for essential needs. Water security through diversified sources provides peace of mind that money can’t buy.
Economic benefits compound over time through multiple value streams. Reduced water bills provide immediate returns on investment. Property values often increase with well-designed sustainable infrastructure that appeals to environmentally conscious buyers. Many municipalities offer rebates, tax credits, or reduced stormwater fees for properties implementing collection systems.
Carbon footprint reduction results from decreased demand for treated municipal water. Municipal water treatment and distribution consume significant energy for pumping, chemical treatment, and infrastructure maintenance. Every gallon of rainwater used reduces this energy demand while eliminating transportation emissions associated with centralized water distribution networks.
How Rainwater Harvesting Systems Work: Components and Scientific Process
How rainwater collection works
How rainwater collection works involves a carefully orchestrated sequence of capture, treatment, and storage processes designed to maximize water quality while ensuring system reliability. Rainwater harvesting system components each serve specific functions that contribute to overall performance and user satisfaction.
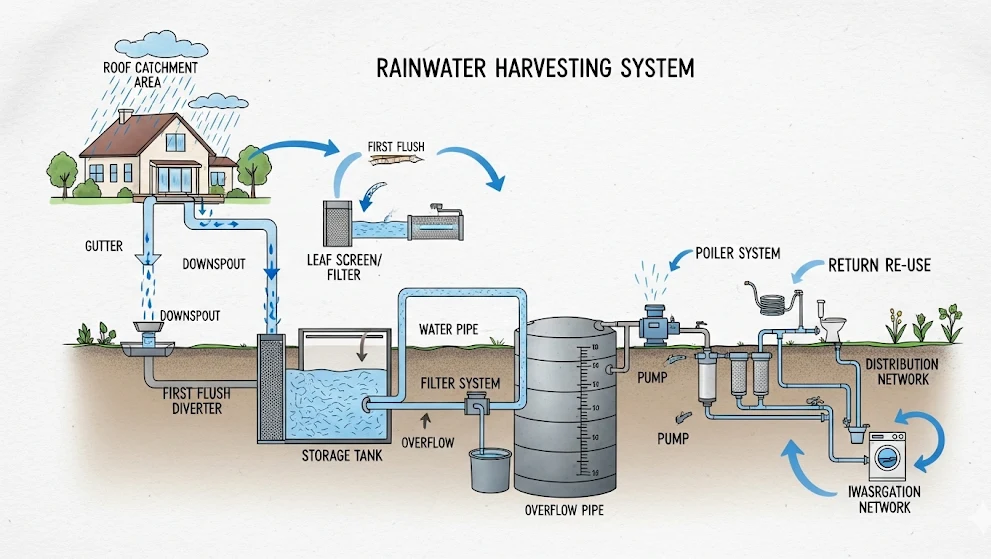
Catchment areas
Catchment areas form the foundation of any collection system, with rooftops providing the cleanest and most efficient collection surfaces. Metal roofing materials shed water quickly with minimal contamination, while asphalt shingles require additional filtration but work adequately for most applications. Roof collection systems can capture 623 gallons from each inch of rainfall on a 1,000 square foot surface, assuming 85% collection efficiency.
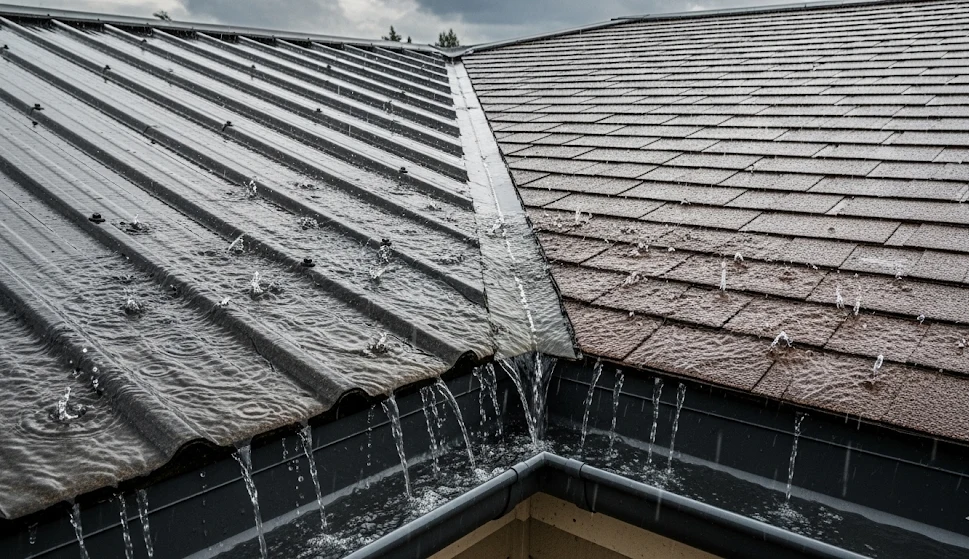

The collection process begins when precipitation contacts catchment surfaces and flows toward drainage points. Surface materials significantly affect water quality and collection efficiency. Metal roofs contribute minimal contamination while providing excellent water shedding characteristics. Clay tiles offer good collection potential but may contribute mineral content that affects water chemistry. Asphalt shingles release some petroleum-based compounds initially but stabilize after weathering.
Gutters and conveyance systems
Gutters and conveyance systems channel collected water from distributed catchment areas toward centralized storage locations. Properly sized gutters prevent overflow during heavy rainfall events that could waste significant collection opportunities. Downspout installation must accommodate peak flow rates while directing water efficiently toward treatment and storage components.

Filtration and treatment processes
Filtration and treatment processes ensure collected water meets quality standards for intended applications. First-flush diverters automatically discard initial rainfall that carries the highest concentration of roof contaminants, bird droppings, and atmospheric pollutants. This simple component dramatically improves stored water quality by eliminating the most contaminated portion of each rainfall event.
Multi-stage filtration removes progressively smaller particles and contaminants through successive treatment steps. Coarse mesh screens catch leaves and large debris at gutter entry points. Sediment filters remove particles that could cloud water or damage downstream equipment. Advanced systems include carbon filtration for taste and odor control plus UV sterilization for biological contaminant elimination.

Storage solutions
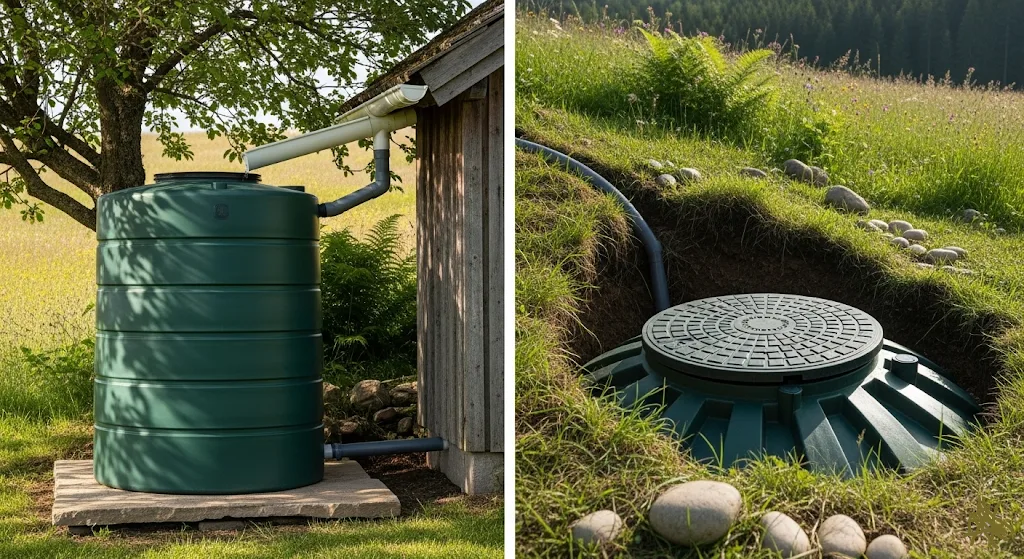
Storage solutions preserve collected water while maintaining quality during extended storage periods. Above-ground tanks provide easy access and lower installation costs but may experience temperature fluctuations and algae growth without proper protection. Underground storage maintains consistent temperatures and eliminates freeze concerns while maximizing space utilization.

Distribution methods
Distribution methods move stored water to application points using gravity pressure or mechanical pumping systems. Simple gravity-fed systems work well for garden irrigation and other low-pressure applications. Pump systems provide pressurized delivery suitable for household plumbing integration and automated irrigation controllers.

Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems: Choosing Your Perfect Match

Types of rainwater harvesting systems accommodate every budget level, technical comfort zone, and space constraint imaginable. Rainwater collection methods range from weekend DIY projects to sophisticated automated installations that integrate seamlessly with smart home technology.
Rain barrel systems
Rain barrel systems provide the perfect entry point for homeowners exploring water collection possibilities. These beginner-friendly installations connect directly to existing downspouts and store 50-80 gallons of water for garden irrigation. Installation requires minimal tools and can be completed in a few hours. Multiple barrels link together through overflow connections, creating expandable systems that grow with changing needs and confidence levels.
Simple rain barrel setups cost $50-200 and deliver immediate water bill savings for households with significant outdoor watering needs. Water storage capacity calculations show that even basic barrels provide substantial irrigation water during typical growing seasons. Many homeowners discover that rain barrel success motivates expansion into larger, more sophisticated collection systems.
Dry systems for direct collection eliminate underground piping by positioning storage tanks close to downspout discharge points. Water flows directly from roof collection areas into nearby tanks without intermediate storage or pumping requirements. These systems empty completely between rainfall events, reducing mosquito breeding potential while simplifying maintenance procedures.
Dry systems for direct collection
Dry system installations work particularly well for properties with straightforward building layouts and adequate space near downspout locations. Tank placement flexibility allows optimization for both collection efficiency and aesthetic integration with existing landscaping. Modular storage systems enable capacity expansion without major infrastructure modifications.
Wet systems for complex setups accommodate buildings where optimal tank placement requires underground piping networks. These installations transport water from multiple collection points to centralized storage areas that may be hundreds of feet from catchment surfaces. Wet systems cost more initially but offer superior flexibility for properties with challenging layouts or space constraints.
Underground piping in wet systems remains filled with water between rainfall events, requiring careful design to prevent freezing damage and maintain water quality. Automatic switching systems can integrate wet collection networks with municipal water supplies for seamless household service during extended dry periods.
Underground storage systems
Underground storage systems maximize collection capacity while preserving valuable above-ground space for other property uses. These installations integrate invisibly with landscaping and protect stored water from temperature extremes that affect above-ground tanks. Underground systems typically provide the largest storage capacities and longest service life.
Smart and automated systems represent the cutting edge of residential water management technology. These sophisticated installations include sensors monitoring tank levels, water quality, and system performance. Smartphone apps provide remote monitoring capabilities while automated controls optimize water distribution based on weather forecasts and usage patterns.
Advanced automation features include weather-responsive irrigation scheduling, automatic switching between water sources, and predictive maintenance alerts. Smart monitoring systems learn household water usage patterns and adjust collection and distribution strategies accordingly. Integration with home automation platforms creates seamless water management that requires minimal user intervention.
Conclusion: Begin Your Water Independence Journey
Rainwater harvesting transforms every rainfall into an opportunity for water conservation and cost savings. Whether starting with a simple rain barrel or planning a comprehensive collection network, these systems provide immediate benefits while building long-term water security.
The path forward involves assessing your property’s collection potential, understanding local regulations, and selecting appropriate system components for your specific needs and budget. Sustainable water practices start with single steps that grow into comprehensive resource management strategies over time.
Ready to reduce your water bills while protecting the environment? Start researching local rainfall data and measuring your roof area today. Every gallon collected brings you closer to water independence and a more sustainable lifestyle that benefits both your wallet and the planet.

click to learn trends – Well-written posts, trends and business updates feel accessible and organized.
market insight click – Articles are practical and help track changes in business effectively.
flow of momentum – Practical and approachable, showing how releasing energy strengthens overall forward movement.
partnership planning click – Guidance is clear, I feel ready to make better decisions.
allianceinsider – Practical and informative, shows structured methods for networking with professionals.
growthstrategieshub – Practical and actionable, partnership strategies are clearly presented for immediate use.
trusted connections hub – Very clear content, networking with peers is natural.
quickbuyhub – Very easy to use, shopping online feels smooth and effortless.
strategic alliance insights – Very useful content, forming alliances feels clear and achievable.
retailhub – Very user-friendly, shopping for products online is fast and intuitive.
retailnavigator – Practical and fast, buying items online is easy to manage.
strategic business network – Useful platform, supports the growth of reliable business alliances.
scalable learning network – Provides ideas for structured learning and growth in a practical way.
international shopping infrastructure – Solid system designed to support large-scale e-commerce globally.
discountbuyhub – Very easy to navigate, finding value purchases is fast and clear.
bondadvisor – Useful and clear, commercial bond strategies are structured for real-world application.
PlanYourFuturePortal – Supports structured and goal-oriented strategic thinking for businesses and individuals.
GrowthStrategyClick – Very informative, helped me understand business scaling clearly.
online savings hub – Transparent pricing with easy-to-follow product comparisons.
modern e-commerce experience – Interface is clean and keeps visitors interested in exploring products.
SavvyDealsHub – Focuses on affordability and convenience for online buyers.
learning made easy – Designed to inspire growth while keeping things clear.
browse yavlo – Pages respond quickly, intuitive layout, very user-friendly experience
trustedconnections – Useful and structured, guidance for building meaningful professional relationships is provided.
landing page – Clear layout, content is concise and browsing feels effortless
SavvyBuyHub – Encourages smart spending with high-value shopping choices.
main hub – Light layout, organized sections, very easy to navigate
global e-commerce portal – Feels designed for an international audience with diverse products.
web destination – Minimal design and quick performance kept my attention
alliancesacademy – Practical guidance, corporate partnerships are presented clearly and effectively.
SavvyDealsHub – Focuses on affordability and convenience for online buyers.
executive business hub – Professional impression conveys trust and effective corporate networking.
engine of motion – Smooth and practical, showing how energy and focus drive progress.
handy link – Clean design, sections are easy to scan and understand quickly
visionary planning site – Offers guidance that aligns with forward-thinking and strategic foresight.
]businessbridge – Informative and logical, the platform presents partnership strategies clearly.
SmartDealsHub – Offers a platform for shoppers seeking the best value purchases.
online entrepreneurial skills – Demonstrates that essential business learning is now highly accessible.
decisionhelperguide – Structured and actionable advice for making smarter choices.
SimpleClickShop – Offers straightforward digital shopping with minimal steps.
resource page – Pages load quickly, simple structure, browsing feels natural
SmartShopCenter – Projects reliability and good value for online purchases.
nexra.click – Simple layout, smooth navigation, very easy to browse today
handy page – Fast-loading pages, minimal clutter, information is straightforward
SmartSavingsCart – Highlights smart and value-focused shopping experiences.
DigitalPurchaseGuard – Security-centric approach reassures users throughout their buying journey.
OpportunityForesight – Helps users evaluate potential directions and prepare for future challenges.
PracticalPathways – Encourages actionable, step-by-step strategies that deliver measurable outcomes.
RixarFlow – Smooth browsing, responsive pages, and information easy to find.
resource page – Clear sections, fast-loading pages, content is easy to digest
PlavexLink – Interface clean, pages responsive, and navigation effortless.
QuickMorixoClick – Smooth pages, organized layout, and finding products was effortless.
explore here – Pages are well-structured, navigation is simple and natural
main hub – Pages open fast, intuitive navigation, all information presented clearly
Ravion Bonded online platform – The site feels organized, and updates are timely and helpful.
Kryvox Capital web page – Clear sections, intuitive layout, and the site exudes a professional, trustworthy vibe.
Cavix official website – Easy navigation and a simple structure make the message easy to understand.
Kryvox Trust official page – Responsive pages, intuitive navigation, and important information is easy to find.
visit yavlo – Pages load quickly, information is presented clearly and logically
globalenterprisealliances – Informative platform, global alliance strategies are explained clearly and practically.
Ulvix main site – Concise content and a tidy layout make navigation smooth.
featured link – Snappy load times and a simple presentation stood out
Explore the official site – Everything reads smoothly and appears carefully put together.
Qulavo Capital Web – Simple navigation, clear headings, and information is presented neatly.
check quvix – Well-organized pages, intuitive navigation, very user-friendly
Home – Pages load quickly, layout is clear, and visitors can navigate content effortlessly.
Community – Sections are well organized, navigation is smooth, and content is simple to explore.
Services – Organized pages and smooth navigation ensure users can browse efficiently.
this capital website – Well-laid-out content makes finding answers uncomplicated.
FAQ – Intuitive menus, pages load fast, and answers are easy to find.
visit zentrik – Pages load smoothly, sections are well-organized and readable
yaverobonding.bond – Nice experience overall, pages are organized and fairly user friendly.
official site – Simple structure, responsive pages, everything works as expected
View bond details – Well-organized pages, stable navigation, and clear site information.
explore now – Smooth interface, quick pages, content is concise and readable
zylavoline insight – Quick site speed enhances the clarity of the main message.
CoreBridge Link – Layout and wording project authority and clarity effectively.
project zorivoline – Suggests potential value as more details are revealed.
start moving ideas – Wording motivates translating creative thought into real action.
MorixoEase – Interface organized, pages smooth, and browsing is very user-friendly.
Vector Hub – Polished interface, easy-to-follow design enhances user experience.
growth hub – Messaging highlights progress and direction, making the focus on growth feel tangible.
learn about zylavobond – Organized content makes it simple to locate key information quickly.
start with zylavoline – Immediate page response and simple messaging make navigation easy.
VixaroEase – Smooth navigation, pages open quickly, and categories easy to browse.
Ideas Execution Hub – Inspiring guidance helps users implement concepts practically and efficiently.
ClickTrivox – Interface clean, links worked perfectly, and browsing was straightforward.
mindful moving guide – Feels grounded and practical, pushing me toward smarter choices.
Official trust hub – The site’s structure is clear, and details are easy to understand.
Future Access – Clean design and focused messaging inspire confidence and engagement.
purpose path portal – Well-structured content helps you see the bigger picture.
everyday savings shop – Very convenient, finding good deals is quick and stress-free today.
Business progress resource – Looks well laid out and easy to understand.
Mavero Trustline online hub – Clear design, organized content, and navigation is straightforward for visitors.
Modern collaboration site – Everything appears well-arranged and simple to understand at first glance.
OBDNet tech hub – Informative and clear, the site simplifies car diagnostic processes.
socialbridge – Excellent for finding and connecting with people who share your passions.
easy purchase tips – Clear process and reliable navigation improved the buying experience.
forwardgreenenergy – Tips that made energy use smarter and more efficient daily.
networkingprofessionals – Great experience, streamlined my professional connections effectively.
corporatealliancehub – Implementing these solutions improved project coordination quickly.
growthventureshub – Very practical advice, helped me plan potential business ventures effectively.
alliancenetworkguide – Helpful platform for managing and expanding business partnerships.
businesslinkup – Smooth experience connecting with like-minded professionals.
Travel Texture Experiences – Vibrant and inviting, content feels genuine and visually appealing.
Classic car Fiat portal – Lively presentation, the posts show genuine enthusiasm for vintage models.
careerpathfinder – Very clear guidance that helped me plan my next steps confidently.
online trusted deals – Deals were quick to find and buying them was very convenient.
Cricket match tracker – Informative layout, fixtures are always up-to-date.
alliancestrategies – Clear strategies that made partnership planning much simpler.
fastbuyportal – Practical and easy to use, checkout was a breeze.
simpleshopclick – Smooth checkout with consistently fast delivery.
smartdigitalstore – Fast, intuitive system for purchasing premium digital items.
online sports hub – Interesting discovery, content appears recent and worth another look.
animated site link – Dropped in randomly, loading is quick and navigation feels natural.
educational support site – I found the information helpful, clear, and presented with compassion.
exploring Manisa – Everything loads quickly and the information is concise and useful.
glass art showcase – The vibe is appealing and the work looks high quality.
RI Tech info – Well structured, easy to absorb tech content without distractions.
Official Barling Collins site – Nicely structured content and transparent messaging around costs.
storytelling showcase – Each project is engaging, well-crafted, and emotionally resonant.
a href=”https://qulavoholdings.bond/” />QulavoPro – Easy navigation and trustworthy information make exploring stress-free.
RixaroPortalPro – Simple and clear interface makes accessing tools effortless.
RixaroHoldings – Great information here, saved me a lot of unnecessary searching time.
LixorFlow – Practical and concise advice made the experience smooth and informative.
OrvixDirect – Step-by-step guidance made using the platform easy and enjoyable.
start here – Layout is simple and intuitive, letting me access information quickly.
visit quixo – Dropped in by chance and everything made sense right away, nice experience.
vexaro info – Random visit, but browsing is easy and content is well presented.
main platform – Clean, professional design allows quick access to key content.
check this out – Easy navigation and tidy layout make finding information effortless.
this core platform – Easy to move around and the content is immediately understandable.
main trust site – Brief visit, but the straightforward design stood out.
Quick clicks – Modern design paired with intuitive browsing.
Belvarin hub – Well-curated products and a neat, simple layout.
glintaro.shop – I love the mix of sleek and unique items on this site, always something new to explore.
Birch Bounty favorites – High-quality, natural items with plenty of variety.
Weekend browsing – Perfect spot to scroll and discover something new.
Blanket Bay favorites – Amazing comfort items, very easy to browse and buy.
yavex access – Quick to navigate, interface is clear and content is easy to digest.
Auroriv selections – Clean interface and wide variety of items for a smooth shopping experience.
glintgarden.shop – So many unique garden items, always an enjoyable experience shopping here!
Worth a click – Something different seems to stand out every visit.
Flower picks – Elegant and delightful selection with a smooth shopping experience.
Style upgrade – The collection leans classy without feeling overdone.
Quick shop link – Simple setup and good value without any fuss.
Fresh aesthetic – The design feels trendy and well put together.
Curated treasures – Feels like a carefully chosen collection with real character.
clothing picks shop – Well-organized categories made browsing quick.
Energetic site – The mix of colors and layout is very inviting.
Home favorites – The site feels polished and makes discovering items fun.
everyday honey goods – Came upon it casually, descriptions explain things well.
Spruce Spark Essentials – Modern layout, site is easy to navigate and purchasing was quick and simple.
Starlight Treasures – Lovely interface, browsing categories is quick and finding items was a breeze.
Stitchery Gems – Fun and organized, shopping is simple and the overall experience was enjoyable.
Suave Basket Lux – Modern and vibrant, browsing categories is easy and checkout process was seamless.
Suave Shelf Studio – Modern and vibrant, site feels easy to navigate and shopping experience was smooth.
Useful Gear Online – Feels current, simple, and focused on real-world needs.
Tervina Market – Straightforward browsing, attractive items, and reasonable price points.
Sunny Shopline Hub Picks – Bright layout, browsing was simple and checkout process worked perfectly.
Tidy Treasure Corner – Clean visuals make the experience feel smooth.
Tidy Treasure Space – The uncluttered look makes browsing comfortable.
Tea Terminal Boutique – Inviting vibe, items are easy to locate and shopping experience is seamless.
Tool Tower Catalog – Clear layout that makes tools easy to compare.
Passport Essentials Hub – Handy gear for trips, navigating and selecting products felt effortless.
Shop Mod Mosaic – Interesting modern designs, navigating the site was smooth and pleasant.
Mod Mosaic – Loved the contemporary mix here, browsing felt effortless and enjoyable.
SchemaAtelier studio – Practical structure and helpful tools made managing tasks simpler.
Everyday Tech Hub – Nice mix of modern tools that seem genuinely helpful.
Tervina Official Store – The layout feels smooth, products look trendy, and the pricing comes off reasonable.
Tidy Treasure Market – Feels organized and stress-free while looking around.
Tidy Treasure Online Shop – The simple design keeps shopping relaxed.
Tool Tower Gear – Everything looks orderly and well displayed.